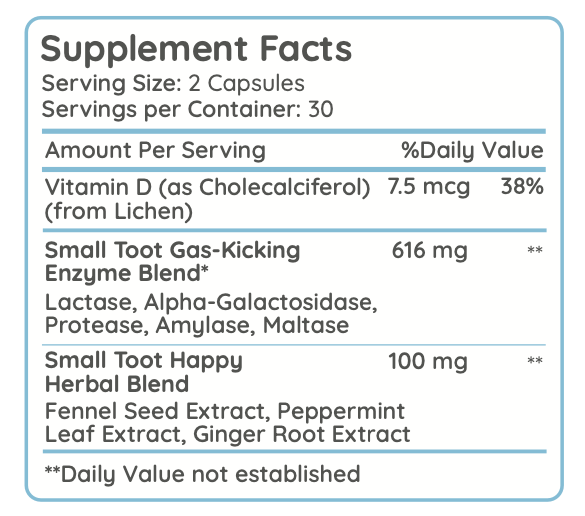
Maltase: A Key Enzyme in Carbohydrate Digestion
Maltase is a crucial digestive enzyme that plays a vital role in breaking down complex carbohydrates into simpler sugars. This enzyme has been the subject of extensive research due to its importance in human nutrition and metabolism.
How Maltase Works
Maltase, also known as alpha-glucosidase, is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of maltose, a disaccharide formed from two glucose molecules[1]. It functions by cleaving the alpha-1,4 glycosidic bonds in maltose, resulting in the release of two glucose molecules[2]. This process is essential for the final stage of carbohydrate digestion, allowing the body to absorb and utilize glucose for energy.
In humans, maltase is primarily produced by cells in the small intestine and is found in the brush border of the intestinal mucosa[11]. It works in conjunction with other digestive enzymes, such as amylase, to break down complex carbohydrates into simple sugars that can be absorbed by the body.
Historical Usage and Discovery
The history of maltase is closely tied to the sugar and starch industry. Its discovery can be traced back to the early 19th century when Napoleon Bonaparte's continental blockade led to a shortage of cane sugar in Europe[2]. This prompted research into alternative sugar sources and eventually led to the identification of various digestive enzymes.
In 1880, H.T. Brown discovered mucosal maltase activity and differentiated it from amylase (then called diastase)[6]. However, it wasn't until the 1960s that advances in protein chemistry allowed researchers like Arne Dahlqvist and Giorgio Semenza to fractionate and characterize small intestinal maltase activities[6].
Scientific Research and Findings
Recent scientific studies have provided insights into the role and importance of maltase:
1. Genetic Variation: Research has shown that maltase activity in humans is primarily attributed to two enzyme complexes: sucrase-isomaltase and maltase-glucoamylase[2][5].
2. Digestion Efficiency: Studies have demonstrated that maltase plays a crucial role in the final stages of starch digestion, converting maltose produced by amylase into glucose for absorption[9].
3. Medical Significance: Maltase deficiency has been linked to certain metabolic disorders. For example, Pompe disease, also known as glycogen storage disease type II, is caused by a deficiency in acid maltase (GAA enzyme)[7].
Industrial and Medical Applications
Beyond its role in digestion, maltase has various applications:
1. Food Industry: Maltase is used in the brewing industry for the production of beers and sake[6].
2. Medical Diagnostics: Maltase activity levels can be used as a diagnostic tool for certain gastrointestinal disorders[8].
3. Potential Therapeutic Target: Research is ongoing into maltase inhibitors as potential treatments for diabetes, aiming to regulate postprandial blood glucose levels[11].
Conclusion
Maltase is a fundamental enzyme in carbohydrate metabolism, with a rich history and ongoing significance in human health and industry. While its primary role in digestion is well-established, research continues to uncover new insights into its genetic variability, potential applications, and role in metabolic disorders.
It's important to note that while maltase plays a crucial role in digestion, individual responses to carbohydrates can vary. Factors such as genetics, overall diet, and gut microbiome composition all contribute to how efficiently one processes starches. As with any aspect of nutrition, a balanced approach tailored to individual needs is recommended.
Sources
[1] Maltase - Enzymes - Our active ingredients - Therascience https://www.therascience.com/en_int/our-active-ingredients/enzymes/maltase
[2] The History of Maltose-active Disaccharidases - PubMed https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29762367/
[3] The Maltase Involved in Starch Metabolism in Barley Endosperm Is ... https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4807107/
[4] Maltase - Enzyme, Structure, Deficiency, and FAQs - Vedantu https://www.vedantu.com/chemistry/maltase
[5] Structural Basis for Substrate Selectivity in Human Maltase ... https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2878540/
[6] Maltase - Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maltase
[7] Pompe Disease History https://www.rarediseaseadvisor.com/hcp-resource/pompe-disease-history/
[8] Metabolic Impacts of Maltase Deficiencies - Wiley Online Library https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1097/MPG.0000000000001955
[9] Maltose Definition, Structure & Function - Lesson - Study.com https://study.com/academy/lesson/maltose-definition-structure-function.html
[10] Maltase - (Anatomy and Physiology II) - Fiveable https://fiveable.me/key-terms/anatomy-physiology-ii/maltase
[11] Maltase – Knowledge and References - Taylor & Francis https://taylorandfrancis.com/knowledge/Medicine_and_healthcare/Physiology/Maltase/